1.1. What is Open Science?
This section presents an introduction to open principles: what is open access, open data, open source - open science?
Introduction to Open Principles
Open Science is the practice of science in such a way that others can collaborate and contribute, where research data, codes and other research outputs are freely available, under terms that enable reuse, redistribution and reproduction of the research and its underlying data and methods. In other words, Open Science means making every step of your research process freely available on the Internet in a way that allows anyone to access and use it - promoting collaboration, reproducibility, transparency and inclusion!
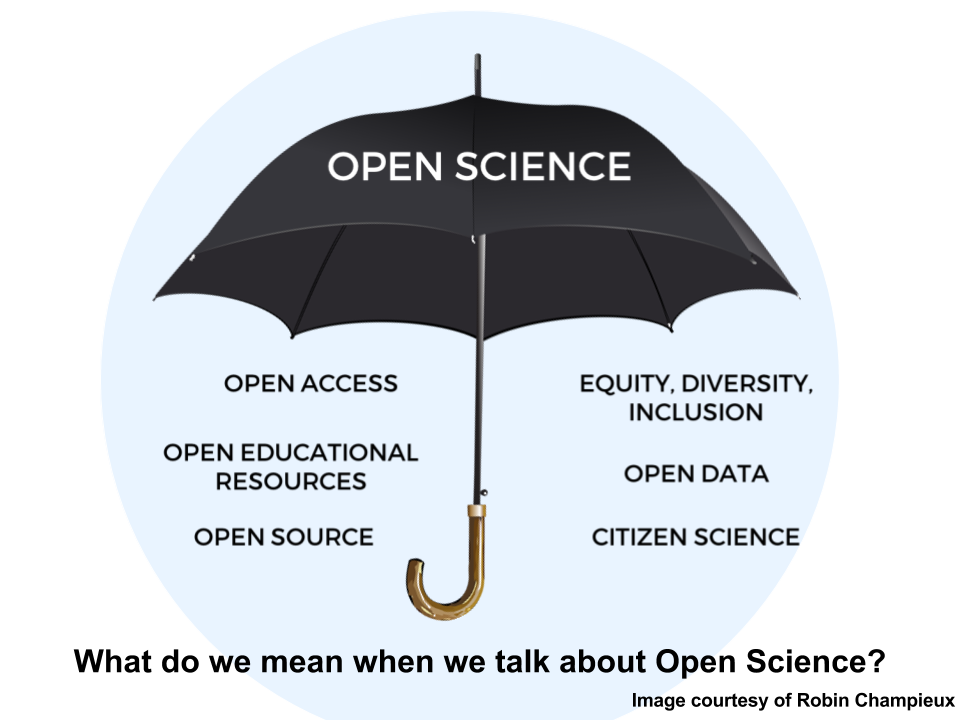
Open Science is an umbrella term for many “open” philosophies and models with the common motivations of sharing freely, preventing duplication, avoiding restrictive (copyright) practices, promoting economic efficiencies and improving access to wide groups of stakeholders.
-
Open Access is free, online access to scientific content (such as peer reviewed publications) with limited copyright and licensing restrictions. An example of this in astrophysics is depositing a version of your manuscript on the arXiv.
-
Open Data is free, online access to data that allows it to be used, reused and distributed provided that the data source is cited. For example, astronomical catalogues and data tables can be published to VizieR.
-
Open Source Software where the source code is freely available online, with terms that allow dissemination and adaptation. The astropy project on GitHub is an example of open source software in astronomy.
-
Open Educational Resources are teaching and learning materials that are freely available online for everyone to use - for example, THIS resource!
-
Citizen Science is research that involves the participation of and contributions by the general public, projects like Galaxy Zoo for example.
-
Equity, Diversity and Inclusion is the most important aspect of the Open Movement through making research outputs accessible to all. Open will mean different things to different communities, so it is extremely important to consider inherent biases in your research projects and how that will affect your results and accessibility to them. Zooniverse has worked to achieve a greater diversity of citizen scientists participating in their project by improving translation tools, adding accessibility functionality, creating a project directly connected to Africa and building a site with a meaningful scientific contribution to the developing world.
Definitions of open principles by FOSTER Open Science and Jisc.
next: Barriers to Open Science